what symbol is used to represent the factor 109?
In the International Organization of Units (SI), each physical quantity—length, mass, volume, etc.—is represented by a specific SI unit. Larger and smaller multiples of that unit of measurement are made past adding SI prefixes. This page shows the most commonly used units, symbols and prefixes. For more details, see Detailed list of metric system units, symbols, and prefixes.
Contents
Units and symbols
| Quantity measured | Unit | Symbol | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length, width, distance, thickness, girth, etc. | millimetre | mm | 1000 mm = 1 m |
| metre | g | ||
| kilometre | km | 1 km = 1000 m | |
| Mass ("weight")* | milligram | mg | grand mg = i thou |
| gram | m | 1000 k = ane kg | |
| kilogram | kg | ||
| megagram (tonne or "metric ton")† | Mg (t) | 1 Mg = i t = 1000 kg | |
| Fourth dimension | second | southward | |
| Temperature | caste Celsius | °C | |
| Area | square metre | thouii | 1 1000two = i m × 1 m |
| hectare | ha | i ha = 10 000 mii | |
| foursquare kilometre | km2 | 1 km2 = 100 ha | |
| Volume | millilitre | mL | 1000 mL = 1 L |
| litre | L | grand Fifty = 1 thousand3 | |
| cubic metre | one thousandiii | 1 m3 = one thousand × one one thousand × ane m | |
| Speed, velocity | metre per second | m/southward | |
| kilometre per hour | km/h | ane km/h = 0.278 m/s | |
| Density | kilogram per cubic metre | kg/10003 | |
| Strength | newton | North | |
| Pressure, stress | kilopascal | kPa | |
| Power | watt | Due west | |
| kilowatt | kW | 1 kW = thousand West | |
| Energy | kilojoule | kJ | |
| megajoule | MJ | one MJ = k kJ | |
| kilowatt-hour | kW⋅h | 1 kW⋅h = 3.half dozen MJ | |
| Electric current | ampere | A | |
| Electric charge | coulomb | C | |
| milliampere-hr | mA⋅h | 1 mA⋅h = 3.6 C |
Notes
* See Is it 'weight' or 'mass'? in the FAQ.
† Run across How most 'tons' and 'tonnes'? in the FAQ for more details.
Prefixes
This table shows the most commonly used SI prefixes. For a complete listing of SI prefixes, including their origins, see SI prefixes and their etymologies.
| Prefix | Symbol | Factor | Ordinary Note | Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| giga | G | x9 | ane 000 000 000 | billion | |
| mega | M | 106 | 1 000 000 | million | |
| kilo | yard | xiii | 1 000 | thousand | |
| 100 | one | i, unity | |||
| milli | m | 10-3 | 0 | .001 | thousandth |
| micro | μ | 10-6 | 0 | .000 001 | millionth |
| nano | n | 10-ix | 0 | .000 000 001 | billionth |
Usage
Although unit of measurement names are ordinary words, notation that unit symbols are but that (symbols) and not abbreviations. They
- are instance-sensitive: uppercase and lowercase letters have different meanings—for example, mm is the millimetre (one-thousandth of a metre), but Mm is the megametre (one million metres);
- don't have atypical and plural forms: information technology's 1 km, 2 km (no "s" at the end);
- have spaces before them: information technology'southward 1 km, not 1km; and
- don't have periods / total stops after them (unless they happen to autumn at the ends of sentences).
For more details on usage, including some common errors, read the USMA's page on correct metric usage. In addition, the FAQ includes some information on usage. For data on typing symbols properly, meet How tin I type unit symbols such equally m2, °C, N⋅m, and µm? in the FAQ.
Examples and relationships
- 1 mL = 1 cm3
- ane millilitre is the aforementioned volume as i cubic centimetre.
- 1 mL of water has a mass of approximately 1 g
- The mass of 1 millilitre of h2o is approximately 1 gram.
- 1 Fifty of water has a mass of approximately 1 kg
- The mass of ane litre of water is therefore approximately i kilogram.
- 1 one thousand3 of h2o has a mass of approximately 1 t
-
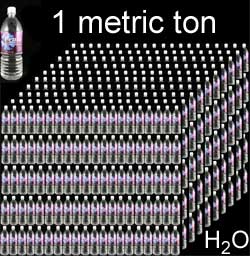
There are 1000 litres in a cubic metre, and then the mass of 1 cubic metre of h2o is approximately grand kilograms or one metric ton.
- The mass of a nickel is 5 g
-

A US nickel weighs 5 grams, and a penny weighs 2.five grams.
- A typical doorknob is 1 m loftier
-

Although in that location's no precise standard for doorknob heights, they're often about i metre above the floor.
- The bore of a CD or DVD is 120 mm
-

A CD or DVD is 120 millimetres across. The diameter of the center hole is 15 millimetres.
- 1 ha = 10 000 m2 (100 grand × 100 yard)
- 1 hectare is 10 000 square metres, equivalent to the area of a square 100 metres on each side. A football field is nearly 100 metres long, so imagine a square the length of a football field on each side, and that'south ane hectare.
Conversion factors
This table gives easily remembered, judge conversion factors for some common units, likewise as more precise factors. Boldfaced values are verbal. Simply call up, estimated values don't warrant precise conversions. If "it was most 100 yards away", so it was about 100 metres away. Merely if it was exactly 100 yards abroad would 1 convert the measurement to 91.44 metres.
| To convert from | to | multiply past | More than precisely, multiply by |
|---|---|---|---|
| acres (US survey) | hectares (ha) | 0.4 | 0.404 687 3 |
| feet (ft) | metres (1000) | 0.3 | 0.3048 |
| fluid ounces (fl oz)* | millilitres (mL) | 30 | 29.573 53 |
| gallons (gal)* | litres (L) | 3.8 | 3.785 411 784 |
| inches (in) | millimetres (mm) | 25 | 25.four |
| knots (kn) | kilometres per hr (km/h) | ane.852 | |
| miles (mi) | kilometres (km) | 1.6 | one.609 344 |
| miles per gallon (mpg) | litres per 100 km [50/(100 km)] | Split 235.215 by mpg | |
| miles per hr (mph) | kilometres per hour (km/h) | 1.6 | 1.609 344 |
| nautical miles (nmi) | kilometres (km) | 1.852 | |
| ounces (oz)† | grams (thou) | 28 | 28.349 52 |
| pound-force (lbf) | newtons (N) | 4.448 222 | |
| pounds (lb)† | kilograms (kg) | 0.45 or divide past 2.ii | 0.453 592 37 |
| pounds per foursquare inch (lbf/inii, psi) | kilopascals (kPa) | 6.894 757 | |
| quarts (qt)* | litres (L) | 0.9 | 0.946 352 946 |
| square feet (sq ft) | square metres (mtwo) | 0.ane | 0.092 903 04 |
| square miles (sq mi) | square kilometres (kmtwo) | 2.half dozen | 2.589 988 |
| yards (yd) | metres (g) | 0.ix | 0.9144 |
Notes
* Fluid ounces, quarts, and gallons refer to US liquid measures.
† Ounces and pounds refer to avoirdupois units.
Final updated:
Source: https://usma.org/commonly-used-metric-system-units-symbols-and-prefixes
0 Response to "what symbol is used to represent the factor 109?"
Post a Comment